Anúncios
The Internet of Things is transforming how we monitor and protect our planet, enabling real-time data collection and analysis for unprecedented environmental insights.
Environmental challenges have reached a critical point in human history. Climate change, pollution, deforestation, and biodiversity loss threaten the delicate balance of ecosystems worldwide. Traditional environmental monitoring methods, while valuable, often fall short in providing the comprehensive, real-time data needed to address these urgent issues effectively. This is where the Internet of Things (IoT) emerges as a game-changing solution, offering innovative approaches to environmental surveillance and conservation.
Anúncios
IoT technology connects physical devices, sensors, and systems through the internet, creating networks that collect, transmit, and analyze data automatically. When applied to environmental monitoring, this technology provides scientists, policymakers, and conservationists with powerful tools to track ecological changes, detect pollution, and implement sustainable practices with remarkable precision and efficiency.
🌍 Understanding IoT’s Role in Environmental Protection
The integration of IoT devices into environmental monitoring represents a paradigm shift from periodic manual measurements to continuous, automated data collection. Smart sensors deployed across various ecosystems can measure temperature, humidity, air quality, water quality, soil conditions, and countless other parameters simultaneously. This constant stream of information creates a comprehensive picture of environmental health that was previously impossible to achieve.
Anúncios
Modern IoT systems utilize wireless communication protocols, cloud computing, and advanced analytics to process vast amounts of environmental data. These technologies work together seamlessly, allowing researchers to identify patterns, predict trends, and respond to environmental threats more rapidly than ever before. The scalability of IoT solutions means they can be deployed in remote wilderness areas, urban environments, industrial sites, and everywhere in between.
The Technical Foundation of Environmental IoT Systems
Environmental IoT networks typically consist of several key components working in harmony. Sensor nodes gather data from their surroundings, measuring specific environmental parameters based on their design and purpose. These sensors can detect everything from particulate matter in the air to chemical concentrations in water bodies, providing granular insights into ecosystem health.
Communication gateways receive data from multiple sensors and transmit it to centralized databases using cellular networks, satellite connections, or other wireless protocols. This infrastructure ensures that even sensors in remote locations can share their findings with researchers and monitoring stations worldwide. The data then flows into cloud-based platforms where sophisticated algorithms process, analyze, and visualize the information for end users.
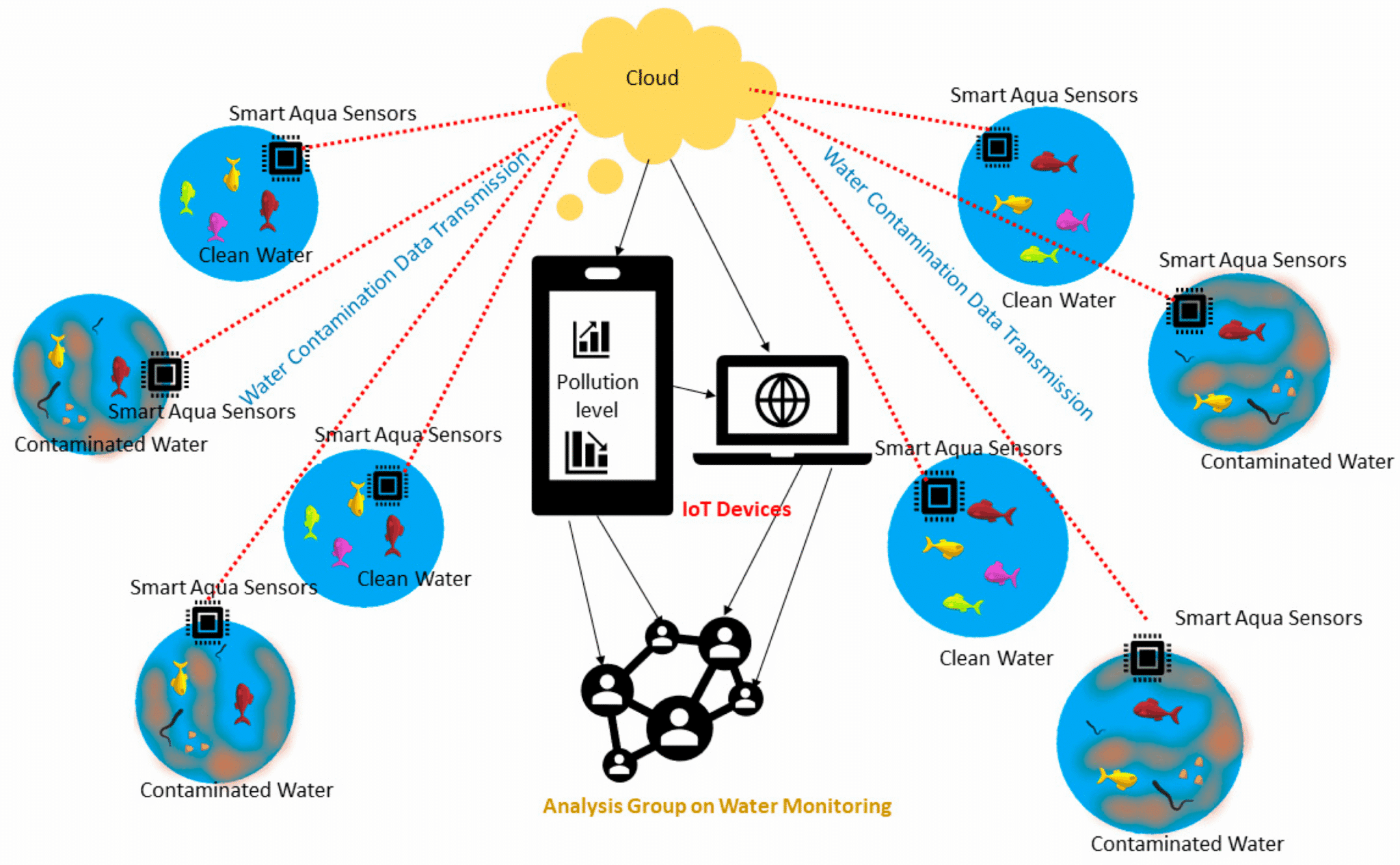
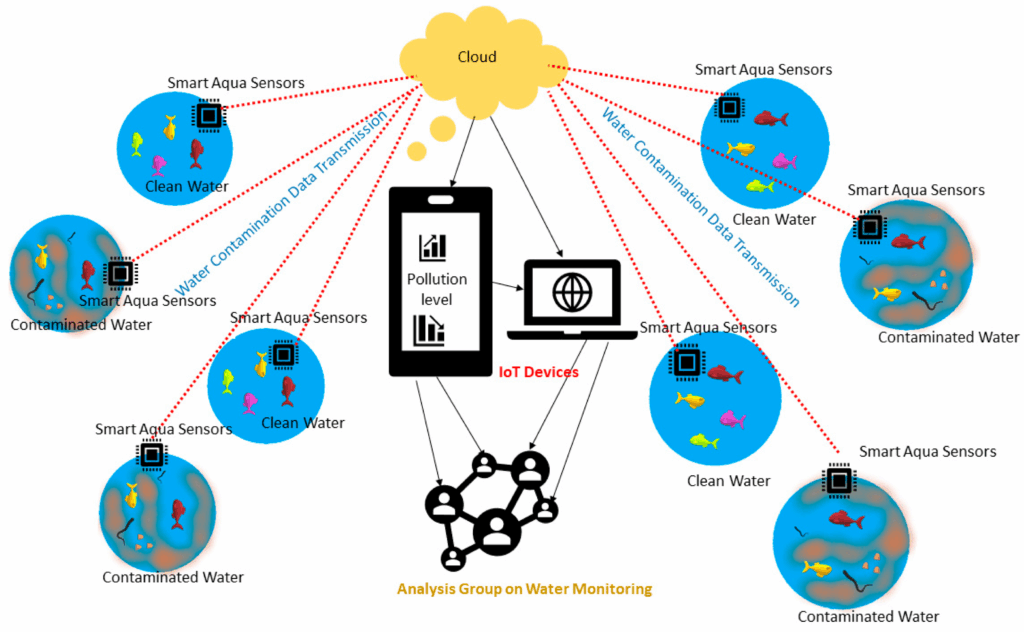
💧 Water Quality Monitoring Through Smart Sensors
Water resources face mounting pressures from industrial pollution, agricultural runoff, and climate-related changes. IoT-enabled water monitoring systems provide continuous surveillance of water bodies, detecting contaminants, tracking pH levels, measuring dissolved oxygen, and monitoring temperature fluctuations that could indicate ecological stress.
Smart buoys and underwater sensors can be deployed in rivers, lakes, and oceans to create comprehensive monitoring networks. These devices transmit real-time data about water quality parameters, enabling rapid response to pollution events. When sensors detect abnormal readings—such as sudden changes in chemical composition or temperature—automated alerts notify authorities who can investigate and intervene before widespread damage occurs.
Agricultural communities benefit significantly from IoT water monitoring systems that track irrigation efficiency and prevent contamination of groundwater supplies. By monitoring water usage patterns and detecting leaks or contamination early, these systems support sustainable farming practices while protecting precious water resources for future generations.
🌬️ Air Quality Management in Smart Cities
Urban air pollution poses serious health risks to billions of people worldwide. IoT-based air quality monitoring networks have become essential tools for cities committed to protecting public health and meeting environmental standards. Dense networks of air quality sensors measure pollutants including particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, ozone, and volatile organic compounds.
These monitoring systems provide hyperlocal air quality data, revealing pollution hotspots that might be missed by traditional monitoring stations. City planners use this information to implement targeted interventions, such as traffic management strategies, industrial emission controls, and green infrastructure projects. Citizens can access real-time air quality data through mobile applications, empowering them to make informed decisions about outdoor activities and protect vulnerable family members.
Integration with Urban Planning and Policy
The data collected by IoT air quality networks informs evidence-based policymaking and urban development strategies. City governments can identify correlations between traffic patterns, industrial activity, weather conditions, and pollution levels, leading to more effective regulatory approaches. Long-term trend analysis helps measure the impact of environmental policies and guides future initiatives.
Green building certifications increasingly incorporate IoT air quality monitoring systems, ensuring that indoor environments maintain healthy conditions. Smart ventilation systems automatically adjust airflow based on real-time pollutant measurements, improving indoor air quality while optimizing energy efficiency—a perfect example of how IoT supports both environmental and economic sustainability.
🌲 Wildlife Conservation and Habitat Monitoring
Protecting endangered species and preserving natural habitats requires detailed knowledge of ecosystem dynamics. IoT technology provides conservationists with unprecedented capabilities for monitoring wildlife populations, tracking animal movements, and detecting threats to biodiversity. Camera traps with wireless connectivity automatically capture and transmit images of wildlife, while GPS collars track animal migrations and behavior patterns.
Acoustic sensors deployed in forests and marine environments record animal sounds, helping researchers monitor species presence and population health without physical intervention. Machine learning algorithms analyze these audio recordings to identify specific species, count individuals, and detect changes in animal behavior that might indicate environmental stress or human encroachment.
Habitat monitoring systems track vegetation health, soil moisture, and microclimate conditions across protected areas. This information helps park managers understand how ecosystems respond to seasonal changes, climate trends, and conservation interventions. Early detection of habitat degradation enables timely action to prevent irreversible damage to critical ecosystems.
🏭 Industrial Emissions and Compliance Monitoring
Industries face increasing pressure to minimize their environmental footprint and comply with stringent emission regulations. IoT monitoring systems provide continuous surveillance of industrial emissions, ensuring compliance while identifying opportunities for operational improvements. Smart sensors measure stack emissions, fugitive releases, and ambient pollutant concentrations around industrial facilities.
Real-time monitoring enables industries to detect equipment malfunctions or process deviations that could lead to excessive emissions before they escalate into serious environmental incidents. Automated reporting systems streamline compliance documentation, reducing administrative burden while maintaining transparency with regulatory authorities.
The economic benefits extend beyond regulatory compliance. By identifying inefficiencies and waste streams, IoT monitoring systems help industries optimize resource utilization, reduce energy consumption, and lower operational costs. This alignment of environmental and economic incentives accelerates the adoption of sustainable industrial practices.
🌾 Agricultural Sustainability Through Precision Monitoring
Modern agriculture must produce more food while minimizing environmental impacts—a challenge that IoT technology helps address through precision farming techniques. Soil sensors measure moisture levels, nutrient content, and pH throughout agricultural fields, enabling farmers to apply water and fertilizers only where and when needed. This targeted approach reduces chemical runoff into waterways while improving crop yields.
Weather stations equipped with IoT capabilities provide hyperlocal meteorological data, helping farmers optimize planting schedules, irrigation timing, and pest management strategies. Integration with automated irrigation systems allows for dynamic water management that responds to actual crop needs rather than fixed schedules, conserving water resources while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Livestock monitoring systems track animal health, location, and behavior, enabling early disease detection and reducing the need for preventive antibiotic use. Environmental sensors in animal housing facilities maintain optimal conditions for animal welfare while minimizing energy consumption and emissions.
⚡ Energy Management and Climate Action
The transition to renewable energy and improved energy efficiency depends heavily on accurate monitoring and intelligent management systems. IoT devices track energy generation from solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable sources, optimizing performance and predicting maintenance needs. Smart grid technologies balance energy supply and demand dynamically, integrating distributed renewable generation while maintaining grid stability.
Building management systems use IoT sensors to monitor occupancy, temperature, lighting, and energy consumption throughout structures. Automated control systems adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on actual usage patterns and environmental conditions, significantly reducing energy waste. The aggregated data from thousands of smart buildings provides valuable insights for urban energy planning and climate mitigation strategies.
Carbon Footprint Tracking and Reduction
Organizations increasingly use IoT systems to measure and manage their carbon footprints comprehensively. Sensors track energy consumption, transportation emissions, waste generation, and other activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. This granular data enables targeted reduction strategies and provides verifiable metrics for sustainability reporting and carbon offset programs.
🔬 Challenges and Considerations in Environmental IoT
Despite its tremendous potential, environmental IoT monitoring faces several challenges that must be addressed for widespread implementation. Sensor accuracy and calibration require ongoing attention to ensure data reliability. Environmental conditions can be harsh, demanding rugged devices capable of operating reliably in extreme temperatures, humidity, and exposure to elements.
Power supply represents a significant challenge for remote sensors. While solar panels and advanced batteries extend operational life, maintaining long-term deployments in wilderness areas requires innovative energy solutions. Researchers are exploring energy harvesting techniques that capture power from environmental sources like temperature gradients or mechanical vibrations.
Data management and cybersecurity concerns grow as environmental monitoring networks expand. The massive volumes of data generated by IoT sensors require efficient storage, processing, and analysis infrastructure. Protecting these systems from cyber threats is crucial, as compromised environmental monitoring networks could provide false information that undermines conservation efforts or public health protections.
🚀 The Future of Environmental IoT Innovation
Emerging technologies promise to enhance environmental monitoring capabilities even further. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are becoming more sophisticated at interpreting environmental data, identifying subtle patterns, and predicting future conditions. Satellite-based IoT communication systems are expanding coverage to the most remote regions, ensuring global environmental monitoring capabilities.
Miniaturization continues to make sensors smaller, cheaper, and more energy-efficient, enabling denser monitoring networks and new applications. Biodegradable sensors made from sustainable materials could eventually be deployed temporarily without environmental impact, while drone-mounted sensors provide flexible, mobile monitoring capabilities for rapid environmental assessments.
Integration across different monitoring systems will create comprehensive environmental intelligence platforms that synthesize data from air quality sensors, water monitors, wildlife cameras, weather stations, and satellite imagery. This holistic approach will provide unprecedented understanding of environmental systems and their interconnections.
🤝 Collaborative Approaches to Environmental Stewardship
The success of IoT environmental monitoring depends on collaboration among governments, industries, research institutions, and communities. Open data initiatives make environmental information accessible to researchers, policymakers, and citizens, democratizing environmental knowledge and enabling broad participation in conservation efforts.
Citizen science projects increasingly incorporate IoT technologies, allowing volunteers to contribute to environmental monitoring through personal devices and community-operated sensors. These grassroots efforts complement professional monitoring networks while raising environmental awareness and engagement.
International cooperation in environmental IoT standards and data sharing protocols ensures interoperability and enables global environmental monitoring initiatives. As environmental challenges transcend national borders, coordinated monitoring and response systems become essential for effective planetary stewardship.
The revolution in environmental monitoring enabled by IoT technology offers genuine hope for addressing our most pressing ecological challenges. By providing comprehensive, real-time environmental data, these systems empower informed decision-making at every level—from individual choices to international policy. The integration of smart sensors, advanced analytics, and automated response systems creates powerful tools for protecting our planet’s precious ecosystems and resources.
As technology continues to evolve and costs decline, environmental IoT solutions will become increasingly accessible to communities worldwide. The vision of a sustainable future supported by intelligent environmental monitoring is not merely aspirational—it is becoming reality through the innovative application of IoT technology. Our collective commitment to harnessing these tools wisely will determine how effectively we can preserve and restore the natural world for generations to come. 🌱